Hardly any other trend is currently changing digital commerce as much as agentic commerce. We recently published a blog post on this topic entitled "Agentic B2B commerce - what the future of B2B commerce is". The combination of autonomous AI agents, automated processes, and intelligent data processing is about to fundamentally change e-commerce, and not just in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.
While many companies are still talking about conversational commerce, agentic commerce is already going one step further: here, agents on both sides of the trade, on the buyer and seller sides, interact with each other autonomously. They identify requirements, negotiate prices, trigger orders, and optimize the entire process in real time. Welcome to the age of Agentic AI Commerce. To this end, Stripe and OpenAI recently developed the Agentic Commerce Protocol (ACP) and published it.
What is Agentic Commerce - and How Does It Work?
Agentic Commerce describes the fully automated interaction between intelligent purchasing and sales agents. These "AI agents in online retail" communicate directly with each other and take on tasks that previously had to be performed by humans: product searches, price comparisons, order approvals, logistics coordination, or after-sales processes.
In technical terms, Agentic Commerce is based on a networked Agentic Commerce platform that communicates with ERP, PIM, CRM, and payment systems via standardized interfaces.
This infrastructure ensures that purchasing and sales agents can access data in real time, carry out secure transactions, and even process payment protocols or automated checkouts independently.
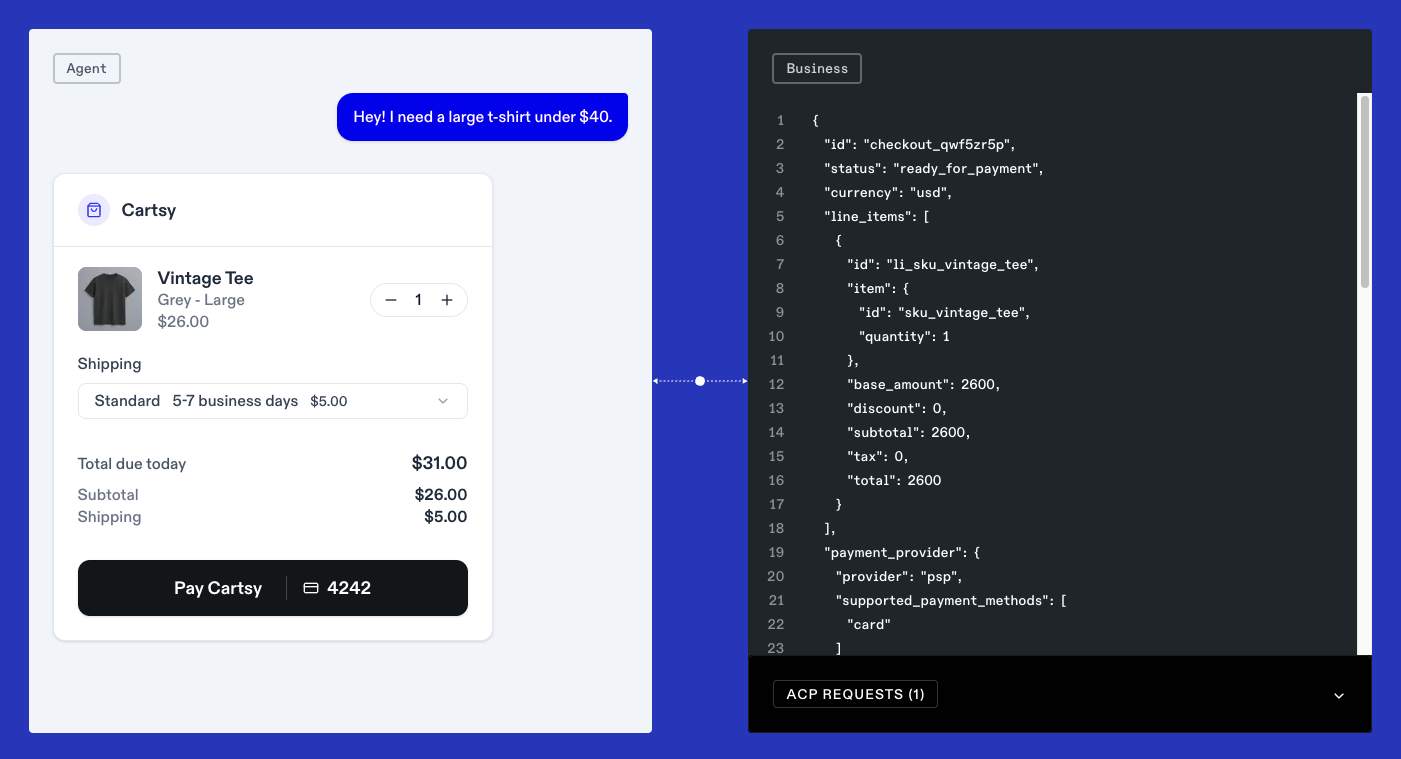
This turns classic e-commerce into a self-learning, autonomous system based on data and rules, not on clicks or manual input.
Why Agentic Commerce is Relevant Right Now
Studies by ECC Cologne show that 2025 is the year in which agentic commerce technologies will move from pilot projects into practice. For B2B companies, retailers, and manufacturers, this means that those who react early to this development will secure a clear competitive advantage and can tap into new sales potential.
Whether in B2B e-commerce, B2C, or wholesale, technology shows its strengths wherever repetitive processes and complex decisions come together. It creates efficiency, precision, and transparency across all channels, from ERP systems to omnichannel sales.
The Opportunities and Challenges for Companies
Opportunities
- Automated purchasing and sales processes reduce costs and increase scalability.
- Data-based decisions improve ROI and enable a more precise customer approach.
- AI agents create new touchpoints and offer entirely new shopping experiences in e-commerce.
The challenges
- Increasing demands on data quality and integration of existing systems.
- Security, data protection, and brand management need to be rethought.
- User acceptance of autonomous agents in purchasing and sales requires cultural change.
In short, agentic commerce not only changes technologies, it changes entire business models.
Technical Requirements and Success Factors
The following building blocks are crucial for the implementation of a successful agentic commerce model:
- Clean data architecture: consistent, structured, and accessible data across systems
- Open system integration: seamless connection to ERP, CRM, PIM, DAM, and payment
- Secure communication protocols, especially for the Agentic Commerce Payment Protocol
- Governance and compliance: clear rules for transparency, control, and liability
- AI expertise within the company: know-how to train and manage AI agents in a targeted manner
Companies that lay these foundations can quickly and efficiently integrate agentic commerce platforms into existing digital retail structures, whether in B2B, B2C, or omnichannel.
Use Cases and Practical Examples
A typical agentic commerce use case is the automated purchasing process: a digital purchasing agent uses stock data to recognize that replenishment is needed. It calls up offers, compares delivery times, negotiates the price, and triggers the order autonomously, including tokenized payment. On the seller's side, the sales agent reacts dynamically to this request, adjusts discounts and delivery conditions, and completes the order all in seconds. This creates a new form of digital commerce: agentic commerce as a self-learning network that is fast, secure, and scalable.
Webinar Tip: Understanding and Implementing Agent-Based Commerce
Together with ECC Cologne/IFH Cologne, we will be giving a compact insight into the future of agent-based e-commerce on November 20, 2025, at 11 a.m.
In the free webinar you will learn
- How agentic commerce technologies are changing e-commerce
- What role AI agents will play in purchasing, sales, and payment in the future
- What strategic and technical steps you should take now
Further information and free registration are available at the following link: https://events.techdivision.com/webinar-agentic-commerce
Conclusion: The Future of E-Commerce is Agentic
Agentic commerce is more than just a fashionable buzzword; it is the logical evolution of digital commerce models. With autonomous AI agents, sophisticated data and system architecture, and a clear agentic commerce strategy, a new ecosystem is emerging that will have a lasting impact on digital commerce.
Whether for retailers, manufacturers, or wholesalers, now is the right time to get to grips with agentic commerce approaches.
Because one thing is certain: the future of e-commerce will no longer be controlled by clicks but increasingly by agents.
Do you have any questions?
Then you can arrange a non-binding consultation with us here.

